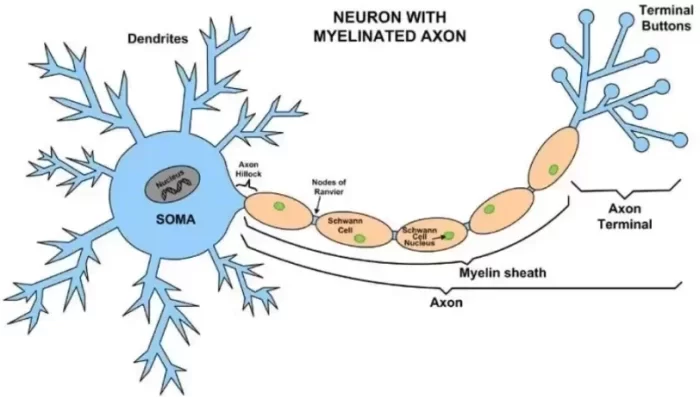
How GABA Functions In Inhibitory Neurotransmission
Experiencing stress, insomnia, or unexplained anxiety? One possible culprit could be a deficiency in GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), an inhibitory neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in calming the brain.
This blog will describe how GABA works to regulate nerve cell activity and why it has such a profound effect on our mental health. Ready for some enlightening information? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of neurochemistry!
Key Takeaways
- GABA is an amino acid that acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain, helping to regulate nerve cell activity and promote relaxation.
- Low levels of GABA have been linked to anxiety, depression, and sleep disorders.
- Medications that target GABA receptors can be used to treat conditions related to low GABA levels.
- Lifestyle changes such as exercise, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can help increase the natural production of GABA.
What is GABA?
GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid, is a neurotransmitter crucial in inhibitory neurotransmission within the central nervous system. It is an amino acid considered the brain’s main inhibitory neurotransmitter.
GABA acts as a natural calming agent, blocking certain nerve impulses and reducing neuronal excitability.
As a neurotransmitter, GABA helps regulate brain activity and promotes feelings of relaxation and calmness. It works by binding to specific receptors on nerve cells, known as GABA receptors, which inhibit nerve cell activity.
This inhibition prevents excessive electrical signals from being transmitted between neurons.
GABA also has important connections to mental health. Low levels of GABA have been linked to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and sleep disorders. In addition to its role in mental health, studies suggest that GABA may also regulate blood pressure and other physical processes.
Understanding how GABA functions can provide insights into potential treatment options for conditions related to low G
Definition
GABA stands for gamma-aminobutyric acid. It’s a special amino acid in your brain and spinal cord. The job of GABA is to quiet things down by stopping nerve cells from firing too much.
This makes it an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which blocks or slows certain brain signals and lowers activity in your nervous system.
Function as a neurotransmitter
GABA is a key part of our nervous system. It acts like a mailman, delivering messages between brain cells called neurons. This process helps to keep everything in balance. GABA works by finding special spots on the outside of neurons where it can stick, known as GABA receptors.
How does this help? When too much activity occurs in your brain, things can get chaotic. So, if brain signals come on too strong or too fast – like at a crazy loud party where everyone is yelling and the music is blaring – that’s when you need GABA to step in.
This helper reduces the noise by slowing down or weakening these intense signals. In short, GABA acts like a calming agent for your busy brain!
GABA and Its Role in Neurotransmission
GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid, is crucial in neurotransmission as an inhibitory neurotransmitter. It functions by blocking nerve impulses and reducing the activity of the central nervous system.
This has important implications for mental health, as low levels of GABA have been associated with conditions such as anxiety disorders and depression. Also, GABA regulates physical health, including blood pressure and immune function.
Understanding the role of GABA in neurotransmission can help guide treatments for conditions related to imbalances in GABA levels. Medications that target GABA receptors are commonly used to treat anxiety and sleep disorders.
Supplementing with GABA or making dietary and lifestyle changes to increase this neurotransmitter’s natural production may also benefit some individuals. However, it is important to consider potential risks and consult a healthcare professional before starting any new treatments or supplements involving GABA.
How it blocks nerve impulses
These receivers control how much chloride can enter the cells. Too much chloride makes it hard for an action potential, or nerve signal, to start. This lowers activity in your nervous system and makes you feel calm and relaxed.
Relationship to mental health
GABA plays an important role in mental health. It helps to regulate nerve cell hyperactivity, which can be associated with anxiety and stress. GABA has a calming effect on the brain and stops messages related to anxiety and fear from being transmitted.
This can help reduce feelings of anxiousness and promote relaxation. Research suggests that oral intake of GABA may have potential benefits in reducing anxiety. However, it’s important to note that more studies are needed to understand the effects of GABA on mental health fully.
If you’re experiencing mental health concerns, it’s crucial to seek professional help for proper evaluation and guidance.
Connection to physical health
GABA is not only important for mental health, but it also has a connection to physical health. It plays a role in metabolism and appetite control. Some studies suggest that GABA may help regulate blood pressure and improve cardiovascular health.
Additionally, low levels of GABA have been associated with conditions like obesity and diabetes. However, more research is needed to understand the relationship between GABA and physical health fully.
Taking care of your overall well-being, including eating a balanced diet and staying physically active, can contribute to healthy levels of GABA in your body.
Treating Low GABA Levels
When it comes to treating low GABA levels, several options are available. A healthcare professional can prescribe medications that target GABA receptors to help increase GABA activity in the brain.
Additionally, some individuals choose to use GABA supplements as a way to boost their GABA levels. These supplements typically come in capsule or powder form and can be taken daily.
It’s important to note that while GABA supplementation may have potential benefits, risks are also involved. Some individuals may experience side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, or headaches when taking these supplements.
As with any supplement or medication, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new regimen.
In addition to medications and supplements, lifestyle changes can also play a role in increasing GABA levels naturally. Engaging in activities such as meditation, yoga, and regular exercise has been shown to affect neurotransmitter function and overall mental health positively.
Eating a diet rich in foods that contain natural sources.
Medications that target GABA
Medications that target GABA can help improve low GABA levels and manage symptoms associated with anxiety. These medications work by increasing the amount of GABA in the brain, which helps to reduce nerve cell hyperactivity and produce a calming effect. Some examples of medications that target GABA include benzodiazepines, such as Xanax and Valium, and certain anticonvulsant drugs, like Gabapentin.
Using GABA supplements
GABA supplements can be beneficial for improving health. They work by increasing levels of GABA in the brain, which helps to regulate neurotransmission. Here are some important things to know about using GABA supplements:
- Treating low GABA levels: GABA supplements are commonly used to treat low levels of GABA in the body. Low GABA levels have been associated with conditions such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia.
- Mood management: GABA supplements may help improve mood by increasing GABA activity in the brain. This can result in feelings of relaxation and calmness.
- Stress reduction: Some studies suggest that GABA supplements may help reduce stress levels by promoting a sense of relaxation and reducing anxiety.
- Anxiety reduction: Research has also shown that GABA supplements may have anxiolytic effects, meaning they can help reduce feelings of anxiety and promote a calmer state of mind.
- Potential benefits: Besides improving mental health, GABA supplements have also been studied for their potential benefits on physical health. For example, they may help lower blood pressure and reduce muscle spasms.
Increasing GABA naturally through diet and lifestyle changes
You can increase GABA naturally through simple changes in your diet and lifestyle. Here are some ways you can do it:
- Eat foods rich in GABA: Incorporate whole grains, beans, nuts, and seeds into your diet. These foods contain the amino acids that help produce GABA in your brain.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity has been shown to increase GABA levels in the brain. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise every day.
- Get enough sleep: Lack of sleep can lower GABA levels in the brain. Ensure you get sufficient sleep each night to support healthy GABA production.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can deplete GABA levels. Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in enjoyable activities.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol intake: Both caffeine and alcohol can interfere with GABA production and function. Try to reduce your consumption of these substances.
Risks and Cautions
It is important to exercise caution when taking GABA supplements, as they can have potential risks and side effects. Some individuals may experience drowsiness or dizziness after taking GABA, while others may have an allergic reaction.
It is also worth noting that the long-term effects of GABA supplementation need to be better studied.
If you are considering using GABA supplements, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting them. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific health needs and ensure it does not interact with any medications you may be taking.
GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid, is a neurotransmitter crucial in inhibitory neurotransmission within the central nervous system. Understanding the risks and cautions associated with GABA can help you make informed decisions about your health.
To learn more about this topic, continue reading our blog post!
Potential risks of GABA supplementation
GABA supplementation may have potential risks, although limited studies have been conducted. It’s important to consider these risks before taking GABA supplements:
- Limited research: There is a lack of extensive scientific studies on GABA supplementation’s long-term effects and safety. This means we don’t fully understand all the possible risks and side effects.
- Interactions with medications: GABA supplements may interact with certain medications, including antidepressants and antipsychotics. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
- Allergic reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to GABA supplements, such as skin rashes or difficulty breathing. If you have known allergies or sensitivities, it’s important to be cautious when trying new supplements.
- Individual reactions: Each person’s body reacts differently to supplements, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s important to monitor your own response to GABA supplementation and discontinue use if you experience negative side effects.
- Quality control: The supplement industry is not heavily regulated, which means there can be variations in the quality and purity of GABA products on the market. Choosing reputable brands and ensuring proper storage of supplements is crucial.
When to seek professional help
If you’re experiencing symptoms related to low GABA levels or mental health conditions associated with GABA dysfunction, it’s important to seek professional help. These symptoms might include anxiety, depression, insomnia, or difficulty concentrating.
A healthcare provider can properly diagnose and determine the best course of treatment for you. They may recommend therapy, medications targeting GABA receptors, or other interventions to help regulate neurotransmitter levels.
Remember, seeking professional help is crucial in addressing underlying issues and finding effective solutions.
Summary and advice from experts
Experts advise caution when considering the use of GABA supplements. While some people may benefit from them, there are associated health risks that need to be considered.
It is important to note that the exact amount of GABA that reaches the brain and its effectiveness are still uncertain. The effects of GABA on mood management, although commonly used for this purpose, are not fully understood.
Therefore, it is recommended to approach the use of GABA supplements with caution and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplementation regimen.
FAQs
1. What is GABA, and how does it function?
GABA, or γ-aminobutyric acid, is a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. It binds to GABA receptors on nerve cells and acts as an inhibitory factor, reducing their activity.
2. How is GABA made in the body?
In our bodies, we make GABA from glutamate with the help of an enzyme called glutamic acid decarboxylase. This process is known as the “GABA shunt.”
3. Can taking GABA supplements have benefits?
Yes! Some people take GABA supplements for their potential benefits, like lowering high blood pressure or treating insomnia symptoms.
4. What are some foods that contain GABA?
Some foods have amounts of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These include chocolates enriched with gamma-aminobutyric acid.
5. How can I boost my levels of Gaba naturally?
One way to increase your level of GABA may be through activities that help your brain relax, such as meditation or yoga, since they target the central nervous system during stressful conditions, which might produce more GABA.
Further Research
1. Gamma-aminobutyric acid, mood disorders, and antidepressants, Romeo B, Choucha W, Fossati P, Rotge JY., Neuropsychiatry Dis Treat. 2018 Sep 3;14:2321-2335. This 2018 review examines the role of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in mood disorders and the effects of antidepressants on the GABAergic system.
2. The Therapeutic Potential of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Receptor Allosteric Modulators, Engin E, Treit D., Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Jan;44(1):213-214. This 2019 review discusses the therapeutic potential of drugs targeting the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) system for anxiety, depression, and cognitive disorders.
3. Gamma-aminobutyric acid, serotonin and dopamine neurotransmission systems alterations in anxiety disorders: A critical review, Nuss P., World J Psychiatry. 2015 Jun 22;5(2):215-32. This 2015 review examines changes in gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), serotonin, and dopamine neurotransmission in anxiety disorders.
4. Gamma-aminobutyric acid as a biomarker for mood disorders: recent developments, Petty F, Kramer GL, Fulton M, Davis L, Rush AJ., Psychiatry Res. 1992 Sep;43(2):121-39. This 1992 study investigates gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) as a potential diagnostic biomarker for mood disorders like depression and bipolar disorder.
5. Gamma-aminobutyric acid mechanisms in schizophrenia, Lewis DA, Hashimoto T, Volk DW., Brain Res Rev. 2005 Feb;48(2):294-304. This 2005 review examines the role of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) dysfunction in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.