Key Takeaways
-
Identify Symptoms Early: Watch for hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, or anaphylactic reactions after consuming amaranth products.
-
Seek Professional Diagnosis: Consult an allergist for proper testing and diagnosis if you suspect an allergy to amaranth.
-
Recognize that individuals allergic to certain foods may also react to amaranth due to cross-reactivity with allergenic proteins and immune responses.
-
Explore Allergy Management: Consider alternative grains like quinoa or rice and carefully read food labels to avoid amaranth.
-
Consult Healthcare Providers: Discuss treatment options and potential risks with healthcare providers to manage amaranth allergy effectively.
-
Adopt a Safe Lifestyle: Take necessary precautions to prevent accidental exposure to amaranth and consider an autoimmune protocol for managing food allergies.
Food allergies can be a real pain, and amaranth allergy is no exception. While this trendy superfood boasts numerous health benefits, it can trigger adverse reactions in some individuals due to its allergenic potential. From hives to gastrointestinal distress, the symptoms of an amaranth allergy and food intolerance can range from mild to severe. But fear not – understanding the signs and managing this allergy is crucial for anyone navigating dietary restrictions. In this post, we’ll delve into the nitty-gritty of amaranth food allergies, exploring symptoms, diagnosis, and practical tips for those with sensitivities.
Identifying Symptoms of Amaranth Allergy
Skin Rash and Hives
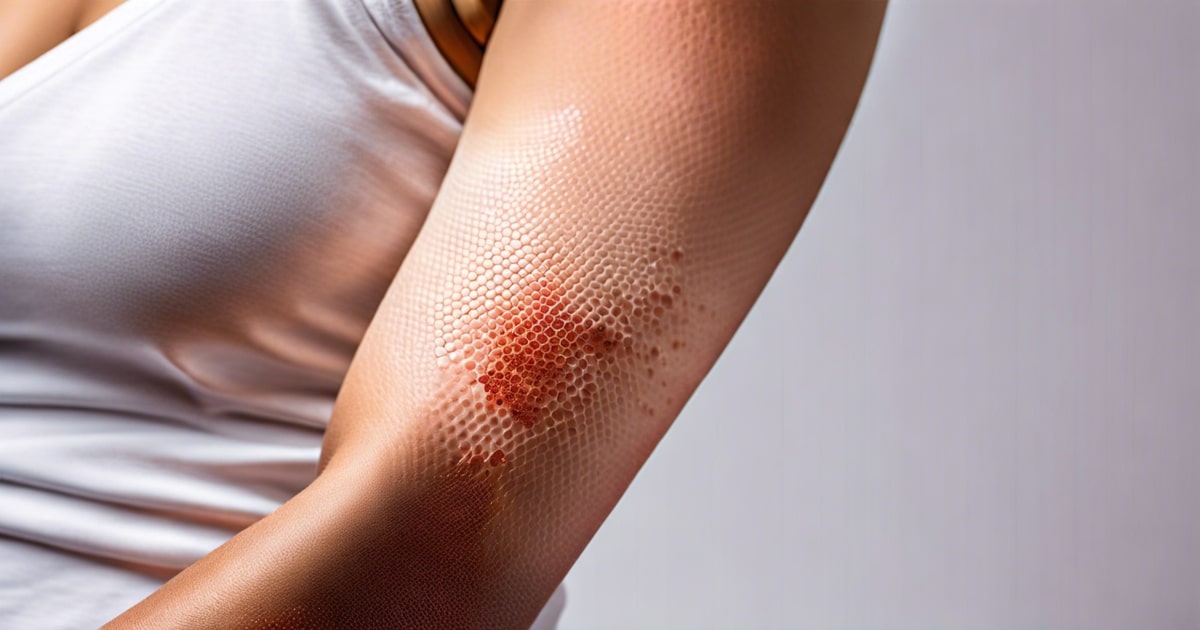
When someone has an amaranth allergy, they might experience a skin rash or hives. This means their skin may become red, swollen, and itchy after consuming amaranth due to food allergy. These allergic responses can be uncomfortable and distressing for the individual.
Amaranth allergy symptoms often include itching, which can be localized to one area or spread across the body. The affected person may feel a strong urge to scratch the itchy areas, but this should be avoided as scratching can further irritate the skin and worsen the reaction.
Digestive Issues
Another common symptom of an amaranth allergy is digestive problems like nausea and vomiting. If someone with this allergy consumes amaranth-containing foods, they may also experience abdominal pain. These symptoms are signs that their body is reacting negatively to amaranth intake.
In some cases, individuals with allergic rhinitis caused by amaranth might also suffer from diarrhea after consuming products containing this ingredient. Therefore, if anyone experiences these digestive issues after eating amaranth-based foods, they should seek medical advice promptly.
Diagnosis of Amaranth Allergy
Allergy Testing

Allergy testing for amaranth allergy typically involves skin prick tests and blood tests. During a skin prick test, a small amount of amaranth extract is placed on the skin, and then the area is pricked with a needle to see if there’s a reaction. Blood tests measure the immune system‘s response to amaranth by detecting specific IgE antibodies.
Skin prick and blood tests are essential in identifying whether an individual has developed a non-allergic reaction to amaranth. For instance, if someone experiences symptoms such as itching or redness at the site where the extract was applied during a skin prick test, it could indicate an allergic response to amaranth.
Keeping a Food Diary
Keeping a food diary can be invaluable in identifying allergic reactions related to amaranth consumption. By documenting all foods consumed and any subsequent symptoms experienced, individuals can identify patterns that may point toward an allergy. This information can provide valuable insights for healthcare professionals when diagnosing potential food allergies.
Maintaining detailed records of food intake and associated symptoms enables individuals to recognize which foods trigger their allergic responses. Noting symptoms like hives or stomach pain after consuming products containing amaranth helps establish connections between specific foods and adverse reactions.
Consultation with an Allergist
Consulting with an allergist is crucial for accurately diagnosing amaranth allergies. An allergist will review medical history, conduct diagnostic tests, interpret results from allergy testing procedures, and provide guidance based on the findings.
Understanding Cross-Reactivity in Amaranth Allergy
Cross-Reactivity with Other Grains
Some individuals with amaranth allergy may also experience cross-reactivity with other grains like quinoa and buckwheat. This means that someone allergic to amaranth might also react when consuming these related grains. People with amaranth allergies need to be aware of this potential cross-reactivity to make informed choices about their diet.
Cross-reactivity occurs when the proteins in one substance are similar to the proteins in another, leading the immune system to mistake them as the same and triggering an allergic response. For example, suppose someone has a known allergy to amaranth and consumes quinoa or buckwheat. In that case, their immune system may recognize the similar proteins in these grains as a threat, causing an allergic reaction.
Latex Allergy and Cross-Reactivity
Individuals who have a latex allergy may also experience cross-reactivity with amaranth. This means their immune system could react similarly to latex and amaranth due to certain protein similarities. Awareness of this cross-reactivity is crucial for those managing latex allergies because it allows them to avoid potential triggers and prevent allergic reactions.
Understanding cross-reactivity is vital for effectively managing allergies. Individuals can make informed decisions about their diet and environment by knowing which substances are likely to cause a reaction due to similarities in proteins. This knowledge empowers them to take proactive measures to avoid allergens and minimize the risk of experiencing severe allergic reactions.
Management and Alternatives for Amaranth Allergy
Avoiding Amaranth-Containing Products
For individuals with an amaranth allergy, the primary management strategy is avoiding consuming products containing amaranth. This means carefully reading food labels before purchasing or consuming any food items. Even a small amount of amaranth can trigger an allergic reaction, so checking ingredient lists is crucial.
It’s important to note that cross-reactivity may occur between amaranth and other grains, seeds, or vegetables due to similar protein structures. Therefore, individuals with amaranth allergies should also be cautious when consuming foods such as quinoa, rice, millet, and other related grains and seeds.
Alternative Grains to Consider
When avoiding amaranth-containing products, individuals can use alternative grains as substitutes. Quinoa is popular because of its nutritional value and versatility in various recipes. It is a complete protein source and provides essential amino acids. Rice is another widely available grain that is a suitable meal replacement for amaranth. Millet offers a nutty flavor profile and can be used in sweet and savory dishes.
Reading Food Labels Diligently To manage an amaranth allergy effectively, individuals must develop the habit of diligently reading food labels on packaged products before purchase or consumption. Look out for terms like “amaranth,” “amaranth flour,” “whole grain amaranth,” or any derivatives of the word “amaranth” on ingredient lists.
Treatment Options for Amaranth Allergy
Antihistamines
When experiencing mild allergy symptoms from amaranth, such as itching or hives, taking antihistamines can provide relief. These medications work by blocking the histamine receptors in the body, reducing symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Over-the-counter antihistamines like loratadine or cetirizine can be effective for individuals with mild reactions to amaranth.
In some cases of amaranth allergy, more severe symptoms like difficulty breathing or swelling of the throat may occur. In these instances, it’s crucial to always have an epinephrine auto-injector on hand. This device delivers a dose of epinephrine to counteract the allergic reaction swiftly and effectively.
Immunotherapy
For those dealing with frequent or severe allergic reactions to amaranth despite avoiding exposure and using medications as directed by a healthcare provider, immunotherapy might be recommended. This treatment involves gradually increasing doses of the allergen under medical supervision to help build tolerance over time.
-
Antihistamines
-
Relieve mild allergy symptoms
-
Block histamine receptors in the body
-
Epinephrine auto-injectors
-
Necessary for severe allergic reactions
-
Deliver a dose of epinephrine swiftly
-
Immunotherapy
-
Recommended for frequent or severe allergies
-
Involves receiving increasing doses of allergen under medical supervision
Safety Concerns for Individuals with Amaranth Allergy
Cross-Contamination Risk
Cross-contamination in food processing facilities poses a risk to individuals with amaranth allergy. Even if a product is labeled as amaranth-free, it may still contain traces due to shared equipment or improper cleaning. This can lead to unintended exposure and allergic reactions.
Individuals with an amaranth allergy must communicate their dietary needs clearly when dining out. They should inform restaurant staff about their allergy and inquire about dish ingredients. By doing so, they can minimize the risk of consuming foods containing amaranth or its derivatives.
Vigilance Is Vital
Vigilance is vital to prevent accidental ingestion of amaranth. Checking food labels meticulously before making a purchase is crucial, as many processed foods, such as flours and concentrates, contain hidden sources of amaranth. Opting for whole foods and preparing meals at home using amaranth-free flour can help mitigate the risk of exposure.
Autoimmune Protocol and Lifestyle Adjustments
Identifying Trigger Foods
When dealing with an amaranth allergy, following an elimination diet can be crucial in identifying trigger foods. This involves removing suspected allergens from your diet and then gradually reintroducing them to observe any adverse reactions. Doing so can pinpoint the specific food causing the allergic response.
For instance:
-
Start by eliminating amaranth-containing products like flour, cereal, or snacks.
-
Gradually reintroduce amaranth-based foods while monitoring for any allergic symptoms.
Maintaining a Well-Balanced Diet
Despite dietary restrictions due to an amaranth allergy, it’s vital to maintain a well-balanced diet. This ensures that your body receives essential nutrients despite certain foods being off-limits. Seek alternative sources of protein, fiber, and other nutrients in amaranth.
Consider incorporating:
-
Quinoa is a substitute for amaranth in recipes.
-
Nutrient-rich vegetables and fruits into your meals to compensate for any nutritional gaps caused by avoiding amaranth.
Carrying Emergency Medication
Lifestyle adjustments may include carrying emergency medication at all times. For individuals with severe allergies, having quick access to epinephrine injectors or antihistamines is paramount in case of accidental exposure to amaranth or cross-contamination.
It’s advisable to:
-
Always carry prescribed emergency medications wherever you go.
-
Educate close contacts about how and when to administer the medication if needed.
The Future of Amaranth Allergy Research
Improved Diagnostic Methods
Researchers are currently dedicated to enhancing diagnostic methods for amaranth allergy. This involves developing more accurate and efficient tests to identify the allergenic potential of amaranth in individuals. These tests aim to provide clearer results, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose allergies more precisely.
Amaranth allergy research also focuses on investigating potential therapies for desensitization. By understanding how the body reacts to amaranth allergens, scientists aim to develop treatments to help individuals build tolerance and reduce their allergic reactions over time. This could significantly improve the quality of life for those with severe amaranth allergies.
Genetic Factors
Understanding the genetic factors contributing to amaranth allergy is a crucial study area. Scientists are exploring how specific genes may influence an individual’s susceptibility to developing an allergy to amaranth. By unraveling these genetic mechanisms, researchers hope to gain valuable insights into the underlying causes of this allergy and potentially identify new targets for treatment or prevention.
Final Remarks
You’ve now comprehensively understood amaranth allergy, from recognizing its symptoms to exploring diagnosis, management, and treatment options. It’s crucial to prioritize your health by staying informed about potential allergens and seeking medical advice if you suspect an allergy. Remember, knowledge is power.
As you navigate the complexities of amaranth allergy, stay proactive in discussing alternative options with healthcare professionals and exploring the evolving research landscape in this field. Your diligence in managing your allergy can lead to a healthier and more fulfilling lifestyle. Stay curious and informed about advancements in allergy research, and don’t hesitate to seek support from communities or professionals specializing in allergies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of an amaranth allergy?
Common symptoms of amaranth allergy may include hives, itching, swelling, and digestive issues. In severe cases, it can lead to anaphylaxis. If you suspect an allergy to amaranth, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
How is amaranth allergy diagnosed?
Amaranth allergy can be diagnosed through skin prick or blood tests to check for specific IgE antibodies. A food diary may also help identify patterns of allergic reactions. Consult with an allergist for accurate diagnosis and personalized guidance.
Can individuals with amaranth allergies consume other similar foods without adverse reactions?
Cross-reactivity in amaranth allergies means some individuals may also react to related foods like quinoa or buckwheat. Working with a healthcare provider or allergist is essential to understand potential cross-reactivity and make informed dietary choices.
What are the alternative options for managing amaranth allergies?
Individuals with amaranth allergies can explore alternative grains like rice, millet, or sorghum as substitutes. Always read food labels carefully and seek advice from a registered dietitian for personalized recommendations on suitable alternatives.
Are there any ongoing research developments in the field of amaranth allergy?
Research into understanding the mechanisms of amaranth allergies and potential treatment options is ongoing. Stay updated on scientific advancements by following reputable sources such as medical journals or consulting healthcare professionals familiar with current research trends.

